In the ever-evolving landscape of technology, few innovations have captured the imagination and promise of a better future quite like blockchain technology. Emerging as the backbone of cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, blockchain has since evolved into a versatile and transformative force, poised to revolutionize industries, streamline processes, and empower individuals worldwide. In this blog, we embark on a journey to unravel the intricacies of blockchain technology, exploring its features, advantages, real-world applications, and the potential it holds for shaping the future of our digital world.
What is Blockchain Technology?
A blockchain is a distributed database or ledger shared among a computer network’s nodes. They are best known for their crucial role in cryptocurrency systems for maintaining a secure and decentralized record of transactions, but they are not limited to cryptocurrency uses. Blockchains can be used to make data in any industry immutable—the term used to describe the inability to be altered.
Because there is no way to change a block, the only trust needed is at the point where a user or program enters data. This aspect reduces the need for trusted third parties, which are usually auditors or other humans that add costs and make mistakes.
Since Bitcoin’s introduction in 2009, blockchain uses have exploded via the creation of various cryptocurrencies, decentralized finance (DeFi) applications, non-fungible tokens (NFTs), and smart contracts.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
- Blockchain is a type of shared database that differs from a typical database in the way it stores information; blockchains store data in blocks linked together via cryptography.
- Different types of information can be stored on a blockchain, but the most common use for transactions has been as a ledger.
- In Bitcoin’s case, blockchain is decentralized so that no single person or group has control—instead, all users collectively retain control.
- Decentralized blockchains are immutable, which means that the data entered is irreversible. For Bitcoin, transactions are permanently recorded and viewable to anyone.
How Does a Blockchain Work?
You might be familiar with spreadsheets or databases. A blockchain is somewhat similar because it is a database where information is entered and stored. But the key difference between a traditional database or spreadsheet and a blockchain is how the data is structured and accessed.
A blockchain consists of programs called scripts that conduct the tasks you usually would in a database: Entering and accessing information and saving and storing it somewhere. A blockchain is distributed, which means multiple copies are saved on many machines, and they must all match for it to be valid.
The blockchain collects transaction information and enters it into a block, like a cell in a spreadsheet containing information. Once it is full, the information is run through an encryption algorithm, which creates a hexadecimal number called the hash.
The hash is then entered into the following block header and encrypted with the other information in the block. This creates a series of blocks that are chained together.
Transaction Process
Transactions follow a specific process, depending on the blockchain they are taking place on. For example, on Bitcoin’s blockchain, if you initiate a transaction using your cryptocurrency wallet—the application that provides an interface for the blockchain—it starts a sequence of events.
In Bitcoin, your transaction is sent to a memory pool, where it is stored and queued until a miner or validator picks it up. Once it is entered into a block and the block fills up with transactions, it is closed and encrypted using an encryption algorithm. Then, the mining begins.
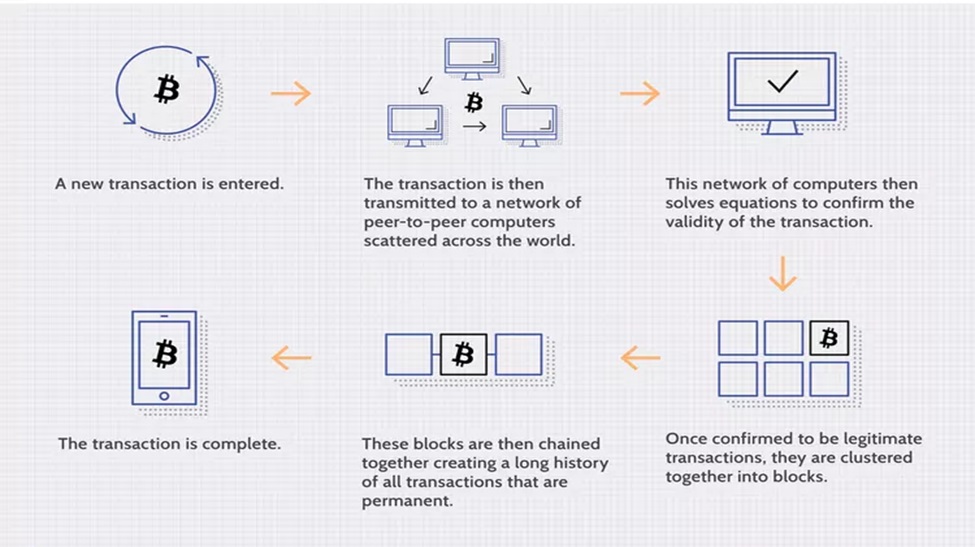
The entire network works simultaneously, trying to “solve” the hash. Each one generates a random hash except for the “nonce,” short for number used once.
Every miner starts with a nonce of zero, which is appended to their randomly-generated hash. If that number isn’t equal to or less than the target hash, a value of one is added to the nonce, and a new block hash is generated. This continues until a miner generates a valid hash, winning the race and receiving the reward.
Once a block is closed, a transaction is complete. However, the block is not confirmed until five other blocks are validated. Confirmation takes the network about one hour to complete because it averages just under 10 minutes per block (the first block with your transaction and five following blocks multiplied by 10 equals about 60 minutes).
Not all blockchains follow this process. For instance, the Ethereum network randomly chooses one validator from all users with ether staked to validate blocks, which are then confirmed by the network. This is much faster and less energy intensive than Bitcoin’s process.
Blockchain Decentralization
A blockchain allows the data in a database to be spread out among several network nodes—computers or devices running software for the blockchain—at various locations. This not only creates redundancy but maintains the fidelity of the data. For example, if someone tries to alter a record at one instance of the database, the other nodes would prevent it from happening. This way, no single node within the network can alter information held within it.
Because of this distribution—and the encrypted proof that work was done—the information and history (like the transactions in cryptocurrency) are irreversible. Such a record could be a list of transactions (such as with a cryptocurrency), but it also is possible for a blockchain to hold a variety of other information like legal contracts, state identifications, or a company’s inventory.
Blockchain Transparency
Because of the decentralized nature of the Bitcoin blockchain, all transactions can be transparently viewed by either having a personal node or using blockchain explorers that allow anyone to see transactions occurring live. Each node has its own copy of the chain that gets updated as fresh blocks are confirmed and added. This means that if you wanted to, you could track a bitcoin wherever it goes.
For example, exchanges have been hacked in the past, resulting in the loss of large amounts of cryptocurrency. While the hackers may have been anonymous—except for their wallet address—the crypto they extracted are easily traceable because the wallet addresses are published on the blockchain.
Of course, the records stored in the Bitcoin blockchain (as well as most others) are encrypted. This means that only the person assigned an address can reveal their identity. As a result, blockchain users can remain anonymous while preserving transparency.
Features of Blockchain
- Decentralization: Blockchain operates without a central authority, distributing control among network participants and reducing the risk of single points of failure or manipulation.
- Transparency: Every transaction on the blockchain is recorded in a public ledger, accessible to all participants, fostering trust, and accountability within the network.
- Immutability: Once a transaction is recorded on the blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted, ensuring the integrity and permanence of data stored on the ledger.
- Security: Blockchain utilizes cryptographic techniques to secure transactions and protect data from unauthorized access or tampering, making it highly secure and resistant to fraud.
- Efficiency: Smart contracts and automated processes on the blockchain streamline transactions, reducing the need for intermediaries and minimizing delays and costs.
- Trustless Transactions: Blockchain enables trustless transactions, meaning parties can engage in transactions without needing to trust each other, as the integrity of the transaction is guaranteed by the blockchain protocol.
Advantages of Blockchain Technology
- Enhanced Security: The cryptographic nature of blockchain ensures secure transactions and data storage, protecting against fraud, tampering, and unauthorized access.
- Increased Transparency: Blockchain’s transparent and immutable ledger provides visibility into transactions, fostering trust among participants and reducing the risk of disputes or errors.
- Reduced Costs: By eliminating intermediaries and automating processes, blockchain technology reduces transaction costs, operational expenses, and the need for manual reconciliation.
- Improved Efficiency: Smart contracts and automated processes on the blockchain streamline transactions, reducing paperwork, processing times, and administrative overhead.
- Decentralization: Blockchain’s decentralized nature removes the reliance on central authorities, reducing the risk of single points of failure, censorship, or manipulation.
- Empowerment of Individuals: Blockchain technology gives individuals greater control over their data and digital assets, enabling self-sovereign identity and decentralized finance (DeFi) solutions.
- Innovation and Disruption: Blockchain technology fosters innovation by enabling new business models, applications, and use cases across various industries, driving economic growth and societal progress.
- Global Accessibility: Blockchain technology facilitates seamless cross-border transactions and access to financial services for individuals who may be underserved or excluded by traditional banking systems. This global accessibility can empower marginalized communities and promote financial inclusion on a global scale.
- Enhanced Data Integrity: Once data is recorded on the blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted, ensuring the integrity and permanence of records. This feature is particularly valuable in industries such as healthcare and supply chain management, where maintaining accurate and tamper-proof records is crucial.
Real-World Applications of Blockchain Technology
- Supply Chain Management: Blockchain is revolutionizing supply chain management by providing end-to-end visibility and traceability. It is used for tracking products from manufacturing to delivery, ensuring authenticity and preventing counterfeit goods.
- Healthcare: In the healthcare sector, blockchain is used for securely storing and sharing patient data, ensuring privacy and interoperability between healthcare providers.
- Voting Systems: Blockchain-based voting systems are being developed to ensure secure and transparent elections, reducing the risk of fraud and manipulation.
- Smart Contracts: Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. They automate processes and eliminate the need for intermediaries, reducing costs and increasing efficiency.
- Digital Identity: Blockchain technology is being used to create decentralized digital identity solutions, providing individuals with control over their personal data and reducing the risk of identity theft.
Drawbacks of Blockchain Technology
- Technology Cost: While blockchain can reduce transaction fees, it’s not without cost. For instance, Bitcoin’s proof-of-work system consumes enormous computational power, using more energy than some countries annually. Some solutions, like using renewable energy sources for mining, are being explored.
- Speed and Data Inefficiency: Bitcoin’s slow processing time limits its transaction capacity to about 3 transactions per second (TPS), far below legacy systems like Visa which can handle 65,000 TPS. Solutions like increased TPS and Ethereum’s upgrades aim to address this issue.
- Illegal Activity: Blockchain’s confidentiality can facilitate illegal trading, as seen with the Silk Road marketplace. While only a small fraction of cryptocurrency transactions are illicit, it remains a concern.
- Regulation: Government regulation poses a threat to cryptocurrencies, though it’s becoming harder to shut down decentralized networks. Still, regulations can impact ownership and usage of cryptocurrencies.
Despite these drawbacks, blockchain technology offers significant benefits, including reduced transaction costs, increased security, and financial inclusion for the unbanked. However, addressing these challenges is crucial for blockchain’s widespread adoption and acceptance.
Challenges and Future Outlook
Moreover, the complexity of implementing blockchain solutions and the need for widespread adoption present additional hurdles to overcome. Interoperability between different blockchain platforms and legacy systems remains a significant challenge, requiring standardization and collaboration across industries. Additionally, the regulatory landscape surrounding blockchain technology is still evolving, with governments grappling with issues such as taxation, data privacy, and consumer protection. Despite these challenges, the future outlook for blockchain technology remains promising, with the potential to revolutionize various sectors and drive continued innovation and disruption in the years to come.
Conclusion
In conclusion, blockchain technology represents a paradigm shift in how we store, transfer, and verify data in the digital age. With its decentralized, transparent, and immutable nature, blockchain has the potential to revolutionize numerous industries, from finance and supply chain management to healthcare and beyond.
As we continue to explore and harness the capabilities of blockchain technology, we embark on a journey towards a more transparent, efficient, and inclusive future. Whether it’s transforming finance through decentralized finance (DeFi), revolutionizing supply chain management, or enabling secure digital identities, blockchain continues to push the boundaries of innovation, paving the way for a truly decentralized and interconnected world.
References
- web.cs.ucdavis.edu/~rogaway/classes/227/spring05/book/main.pdf.
- hackernoon.com/stablecoins-designing-a-price-stable-cryptocurrency-6bf24e2689e5
- medium.com/@argongroup/stablecoins-explained-206466da5e61
- medium.com/coinmonks/asset-tokenization-on-blockchain-explained-in-plain-english-f4e4b5e26a6d
- www.nasdaq.com/article/how-tokenization-is-putting-real-world-assets-on-blockchains-cm767952
- www.investopedia.com/terms/f/fungibility.asp
- www.w3.org/Protocols/Design/Interevol.html